Computer networks are the foundation of modern communication. They connect devices, enable data sharing, and support everything from simple file transfers to complex global operations. Without networks, technologies such as cloud applications, CRM systems, and mobile app development would not function efficiently.
However, not all networks are the same. Each type of network serves a different purpose depending on its size, structure, and usage.
In this article, we will explore the top 10 types of networks and explain how they are applied in real-world scenarios.
What Are the Different Types of Networks?
Before looking into specific categories, it is important to understand what a network is. A network is a system that connects multiple devices, such as computers, smartphones, and servers, to exchange data and share resources. Types of Networks can be classified based on their size, technology, and purpose.
There are generally three main classifications of networks:
- By Size – Ranging from small personal networks (PAN) to global networks (WAN).
- By Medium – Wired networks using Ethernet cables or wireless networks using Wi-Fi and Bluetooth.
- By Functionality – Some are designed for data storage (SAN), while others improve internet speed and content delivery (CDN).
Understanding these categories helps businesses and IT professionals choose the right network for web app development, CRM systems, DevOps, cloud applications, and blockchain development.
1. Local Area Network (LAN)
A Local Area Network (LAN) connects computers and devices within a limited area such as an office, home, or school. It typically uses Ethernet cables or Wi-Fi. LANs are fast, reliable, and cost-effective for small-scale networking.

Uses of LAN
- Connecting office computers for file sharing and printing
- Enabling team collaboration in CMS development projects
- Supporting software testing and QA with centralized resources
Example: Schools use a LAN to provide students access to learning resources and printers.
Source: Cisco – Networking Basics
2. Wide Area Network (WAN)
A Wide Area Network (WAN) covers a large geographical area and connects multiple LANs. The internet is the most prominent example of a WAN. Businesses rely on WANs to connect offices and branches across cities or countries.
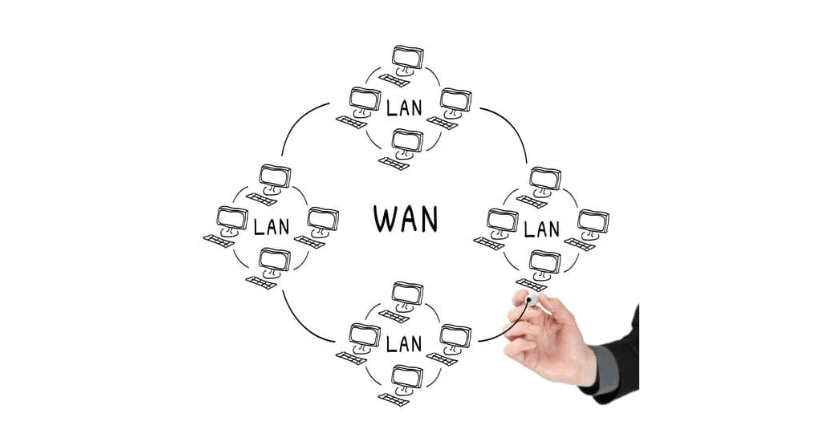
Uses of WAN
- Running global CRM systems
- Connecting corporate offices for business solutions and IT services
- Enabling remote access to cloud applications
Example: Banks use a WAN to connect ATMs with their central servers.
3. Metropolitan Area Network (MAN)
A Metropolitan Area Network (MAN) is larger than a LAN but smaller than a WAN. It usually covers a city or a large campus and is often managed by service providers.

Uses of MAN
- Providing internet access across universities or metropolitan regions
- Supporting city-wide advanced technologies and design projects
- Enabling collaboration for DevOps teams across city offices
Example: Municipalities offering free city-wide Wi-Fi.
4. Personal Area Network (PAN)
A Personal Area Network (PAN) is the smallest type of network. It connects devices around one individual, usually within 10 meters, using Bluetooth or Wi-Fi.

Uses of PAN
- Connecting smartphones, tablets, and wearables
- Helping developers in mobile app development test apps across devices
- Supporting professionals working on blockchain development applications on the go
Example: Pairing wireless earbuds with a smartphone.
5. Virtual Private Network (VPN)
A Virtual Private Network (VPN) creates a secure connection over the internet by encrypting data. It protects privacy and allows safe remote access.

Uses of VPN
- Protecting corporate data during remote work
- Securing business solutions and IT services from cyber threats
- Allowing employees to use cloud applications safely
Example: Companies providing VPN access for remote teams.
6. Storage Area Network (SAN)
A Storage Area Network (SAN) is a high-speed network that connects servers with storage devices. It allows enterprises to manage and store massive amounts of data.

Uses of SAN
- Storing large CRM databases
- Supporting maintenance and support teams with quick backups
- Managing storage for enterprise-level web app development
Example: Hospitals use SANs to store and manage electronic health records.
7. Wireless Local Area Network (WLAN)
A Wireless Local Area Network (WLAN) functions like a LAN but uses Wi-Fi instead of cables. It provides flexibility and mobility for users.

Uses of WLAN
- Offering wireless internet in offices, cafes, and airports
- Supporting device testing in software QA
- Enhancing productivity in mobile app development projects
Example: Public Wi-Fi in airports.
8. Campus Area Network (CAN)
A Campus Area Network (CAN) connects multiple LANs across a corporate, industrial, or educational campus.
Uses of CAN
- Linking university libraries, labs, and dorms
- Connecting departments for CMS development projects
- Supporting centralized cloud applications across a campus
Example: A university network connecting hostels, lecture halls, and research labs.
9. Enterprise Private Network (EPN)
An Enterprise Private Network (EPN) is designed and owned by organizations to connect their internal offices and employees securely.

Uses of EPN
- Managing CRM systems securely across multiple branches
- Supporting collaboration in DevOps projects
- Enabling secure blockchain development activities
Example: Large corporations like Microsoft and Google maintain private enterprise networks for secure operations.
10. Content Delivery Network (CDN)
A Content Delivery Network (CDN) consists of distributed servers that deliver web content quickly by caching it close to users’ locations.

Uses of CDN
- Boosting speed for web app development
- Enhancing user experience for CMS development platforms
- Ensuring high availability for business IT services
Example: Netflix and YouTube use CDNs to stream videos smoothly worldwide.
Source: Cloudflare – What is a CDN
Conclusion
The types of networks we covered play a vital role in both everyday communication and enterprise-level IT operations. From LANs in offices to CDNs powering global video streaming, each network has its own importance. Businesses implementing cloud applications, CRM systems, DevOps, or blockchain solutions must carefully choose the right network to ensure efficiency and security.
If you are looking to strengthen your IT infrastructure, explore our business solutions and IT services designed to meet your networking needs.
FAQs
LAN, WAN, MAN, PAN, VPN, SAN, WLAN, CAN, EPN, and CDN.
LAN and WLAN are the most practical choices.
LAN is limited to a building or office, while WAN covers multiple locations across cities or countries.
It provides secure and encrypted connections for remote work.
It reduces latency and speeds up content delivery.
PAN is personal primarily, but valuable for small device-to-device communication.
WAN and VPN are commonly used for cloud services.
SAN helps enterprises manage, secure, and access large amounts of data quickly.