In today’s digital-first world, the demand for seamless internet connectivity has never been higher. Whether in homes, offices, or enterprise networks, different types of networking devices play a crucial role in ensuring smooth communication between systems.
From simple hubs to advanced firewalls, each device is designed with a specific purpose that contributes to speed, security, and reliability.
Understanding these devices is not only essential for IT professionals but also valuable for businesses investing in cloud applications, DevOps practices, or even mobile app development that relies on robust networks.
This guide explains the most important types of networking devices and their functions, along with practical use cases.
Key Takeaways
- Networking devices enable smooth communication between computers and networks.
- Common types include routers, switches, modems, firewalls, and access points.
- Businesses rely on networking devices for security, scalability, and cloud connectivity.
- Regular updates and upgrades ensure performance and data protection.
- Choosing the right devices supports modern IT solutions like CRM, DevOps, and blockchain development.
What Are Networking Devices?
Networking devices are physical or virtual hardware components that connect, manage, and secure communication between computers, servers, and other digital systems. They act as the backbone of local area networks (LANs), wide area networks (WANs), and even cloud-based infrastructures.
According to Cisco Networking Academy, networking devices ensure data is transmitted accurately and efficiently across multiple nodes in a network. Without them, global connectivity and modern business solutions & IT services would not exist.
Common Types of Networking Devices and Their Functions
1. Hub
A hub is the simplest networking device that broadcasts data to all devices in a network.
- Function: Acts as a central connection point.
- Limitation: Lacks intelligence, causing unnecessary data traffic.
- Best For: Very small or temporary networks.
2. Switch
A switch is more advanced than a hub. It forwards data only to the intended device.

- Function: Uses MAC addresses to direct traffic.
- Benefit: Reduces congestion and increases performance.
- Use Case: Offices, data centers, and enterprise environments.
(Reference: Cisco – Switches Explained)
3. Router
A router connects multiple networks and directs data packets between them.

- Function: Uses IP addresses for data transfer.
- Benefit: Provides internet connectivity to multiple devices.
- Advanced Role: Modern routers include firewalls, VPN, and Wi-Fi support.
4. Modem
A modem connects a local network to the internet using telephone, cable, or fiber lines.
- Function: Converts digital data to analog and vice versa.
- Use Case: Essential for broadband internet connections.
5. Access Point (AP)
An access point provides wireless connectivity in a network.

- Function: Extends wired networks into wireless environments.
- Use Case: Homes, offices, and public Wi-Fi hotspots.
6. Firewall
A firewall is a security device that filters incoming and outgoing traffic.
- Function: Blocks unauthorized access.
- Types: Hardware firewall, software firewall, and cloud-based firewall.
- Importance: Critical for advanced technologies & design where data security is paramount.
7. Gateway
A gateway acts as a translator between different network architectures.
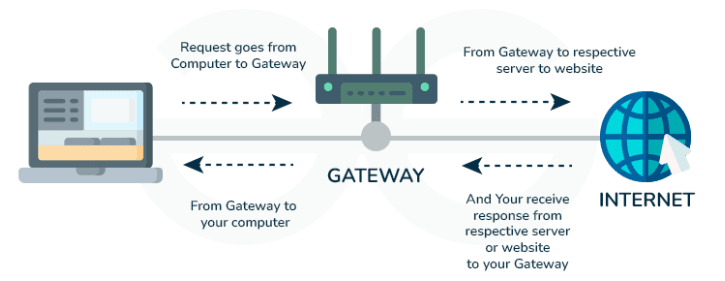
- Function: Connects networks using different communication protocols.
- Use Case: Large-scale enterprise networks and cloud services.
8. Repeater
A repeater boosts weak signals across long distances.
- Function: Extends network coverage.
- Use Case: WAN connections, large buildings, and remote offices.
9. Bridge
A bridge connects two different LAN segments.
- Function: Filters traffic and manages collisions.
- Use Case: Expanding business networks without replacing infrastructure.
10. Network Interface Card (NIC)
A NIC allows a computer or server to connect to a network.
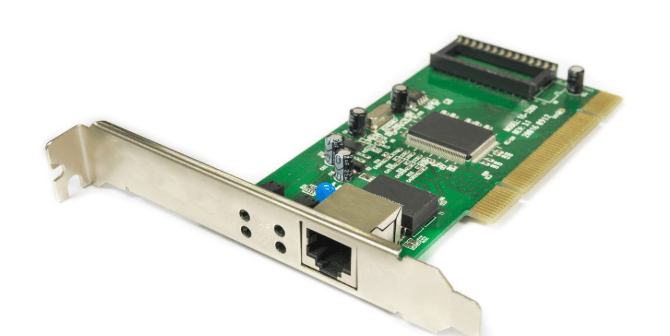
- Function: Provides a unique MAC address.
- Use Case: PCs, laptops, and servers in both wired and wireless networks.
Importance of Networking Devices in Businesses
For businesses investing in CRM solutions, software testing & QA, or blockchain development, networking devices ensure high availability, secure data exchange, and reliable cloud connectivity.
Key benefits include:
- Performance Optimization: Switches and routers improve data flow.
- Security: Firewalls and gateways protect business applications.
- Scalability: Access points, repeaters, and bridges expand networks.
- Support for IT Services: Ensures reliable infrastructure for CMS development, mobile app development, and cloud applications.
Conclusion
Networking devices are the foundation of every modern IT infrastructure. From hubs and switches to firewalls and gateways, each device serves a vital purpose in improving communication, security, and performance. For businesses embracing cloud applications, CRM solutions, or advanced technologies & design, selecting the right devices ensures long-term scalability and resilience.
Whether you’re a beginner or managing enterprise-level business solutions & IT services, understanding the types of networking devices will help you make smarter decisions and build a strong digital ecosystem.
FAQs About Networking Devices
A hub broadcasts data to all devices, while a switch sends it only to the intended device.
Yes. A modem connects you to the internet, while a router distributes the connection.
No. Access points extend wireless coverage but still need a router.
A firewall is essential for blocking unauthorized access and threats.
No. There are also virtual and cloud-based networking devices.
Gateways allow communication between different protocols, crucial for global businesses.
Regular firmware updates are recommended for security and performance.